Introduction
Have you ever wondered whether cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ether could be a good fit for your investment portfolio? Are they essential for diversifying your portfolio, or just a wild rollercoaster ride?
In recent years, cryptocurrencies, led by Bitcoin as the first and most prominent cryptocurrency, have evolved from a niche experiment to a global phenomenon. Last year, and especially following the US elections, cryptocurrencies have experienced an impressive momentum characterized by strong capital inflows from institutional investors into Bitcoin ETFs, indicating that interest in digital currencies is growing. The prospect of regulatory easing and the potential introduction of Bitcoin reserves in the US is further strengthening investor confidence. Many believe that Bitcoin could play a more significant role in the global financial system in the future.
Bitcoin and Ethereum/Ether: differences and similarities
To answer the question of whether cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ether fit into a portfolio, we first examine the differences and similarities between these two digital currencies. Bitcoin and Ether are the most well-known digital currencies, but they serve different purposes. Bitcoin was introduced in 2009 and is, simply put, a digital peer-to-peer payment system that operates without a central authority. It is based on a blockchain, a decentralized, public database that records all transactions. Supporters view Bitcoin as “digital gold,” a hedge against inflation, and a response to distrust in traditional currencies and central banks. They value its decentralization and the limited supply of Bitcoins, which make it a store of value in their view.
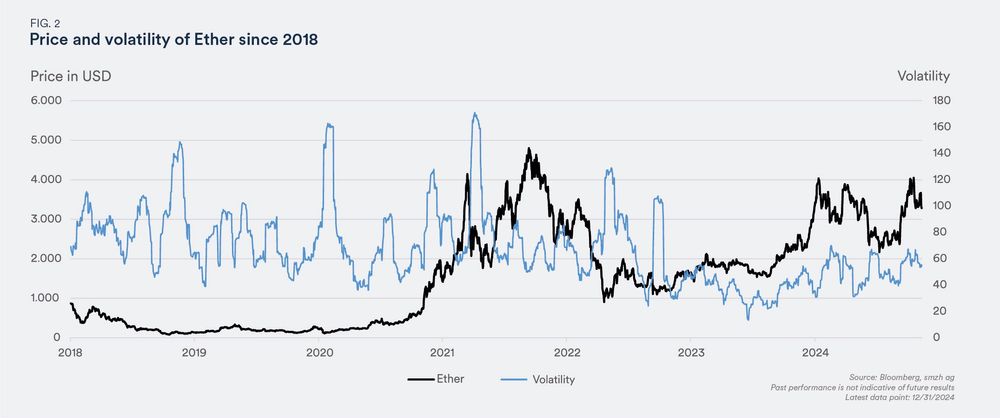
Ethereum was introduced in 2015 and is, simply put, a blockchain platform where programs and contracts can be created. Supporters of Ethereum value the versatility of the platform, which enables many different applications, such as digital art, financial services, and decentralized applications (dApps). Ether (ETH) is the currency used to settle transactions on the Ethereum platform.
The portfolio question: diversification or speculation?
The unique characteristics of Bitcoin and Ether provide an initial hint of how their roles in an investment portfolio might differ. But are they sensible investments, or merely speculative? Should they be considered a serious form of investment, or are they just speculative assets? Critics like Warren Buffett generally reject cryptocurrencies, arguing that they lack intrinsic value and are more speculative assets than meaningful investments. With increasing acceptance among large investors, rising market liquidity, and supportive regulations, this debate is more relevant than ever.
Are cryptocurrencies the missing piece in your portfolio? Let’s analyze the potential and risks together. The following analysis is well-founded, though at times technical and complex – but stay tuned, it will be worth it.
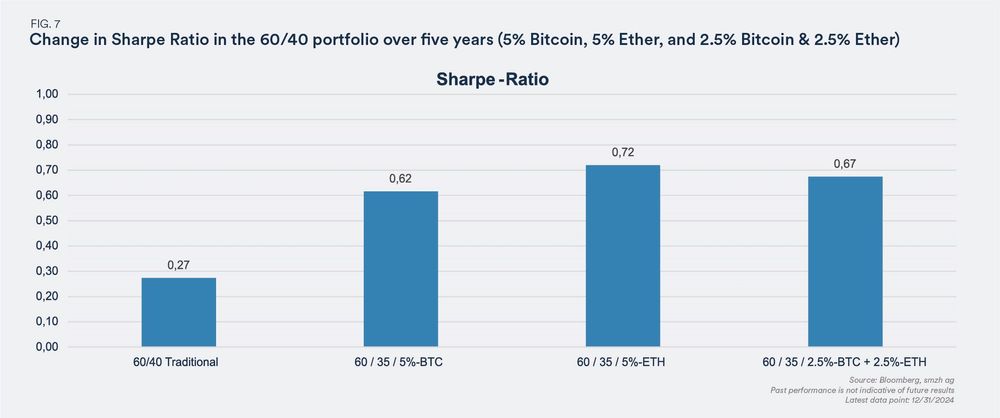
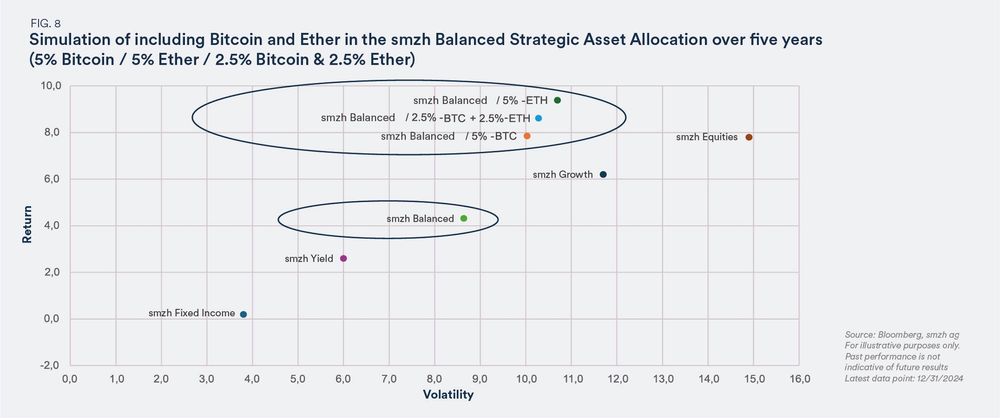
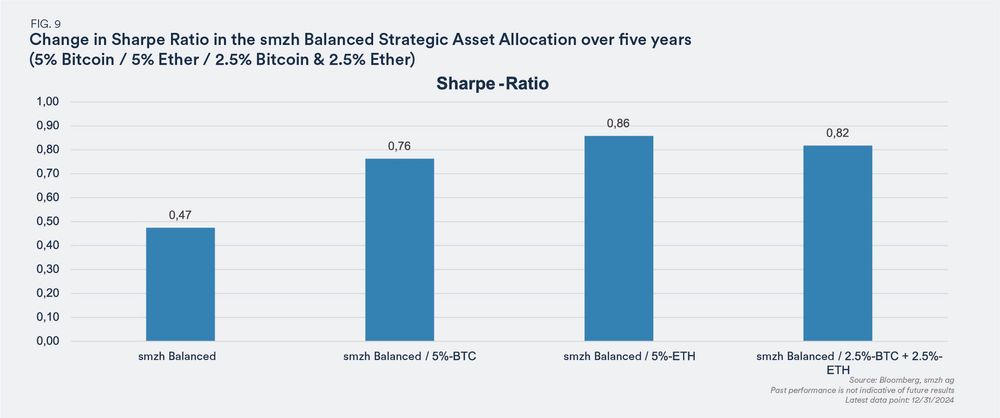
To explore whether cryptocurrencies can add value to a diversified investment portfolio, traditional portfolio theories can help better assess the opportunities and risks.
Performance and Volatility
Analysis of historical returns and price fluctuations
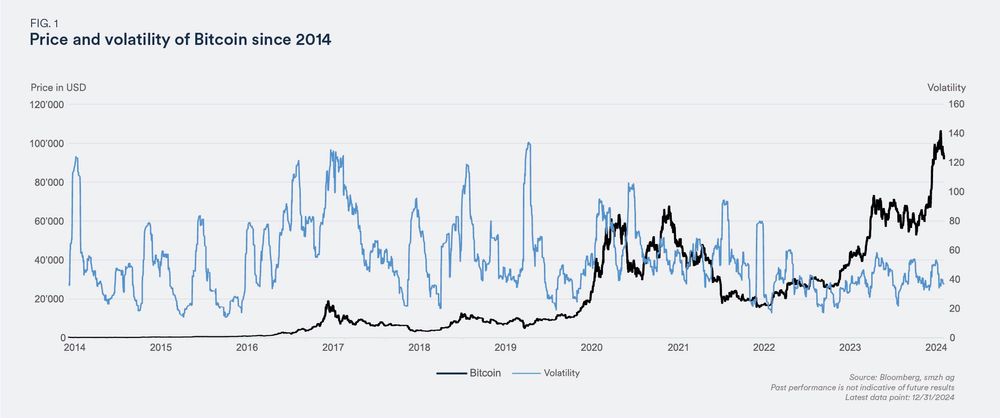
First, we look at the price development of these two cryptocurrencies and their price fluctuations since their introduction. The price of Bitcoin has risen from nearly zero to over USD 100,000 in the last ten years. Historical data shows that Bitcoin has experienced extremely high price fluctuations during this period. The 30-day volatility(1) ranged from 20% to 140%, making Bitcoin one of the most volatile investment instruments. However, these swings may have been compensated for by above-average returns.